
7.3 Important concepts in hypothesis testing - summary.

7.2 Statistically significant result (rejecting H0).6.2.2 Sampling distribution for a sample sum ( \(S\)).6.2.1 Sampling distribution of a sample mean.6.2 Sampling distribution for a statistic (a sample mean, a sample proportion etc.).6.1 Statistics and sampling variability.6 The basics of statistical inference.5.4 Continuous probability distributions - uniform and normal distributions.5.3.2 Some characteristics of the binomial distribution.5.3.1 Binary random variables and Binomial distribution.5.3 Discrete probability distributions - Bernoulli and binomial distributions.
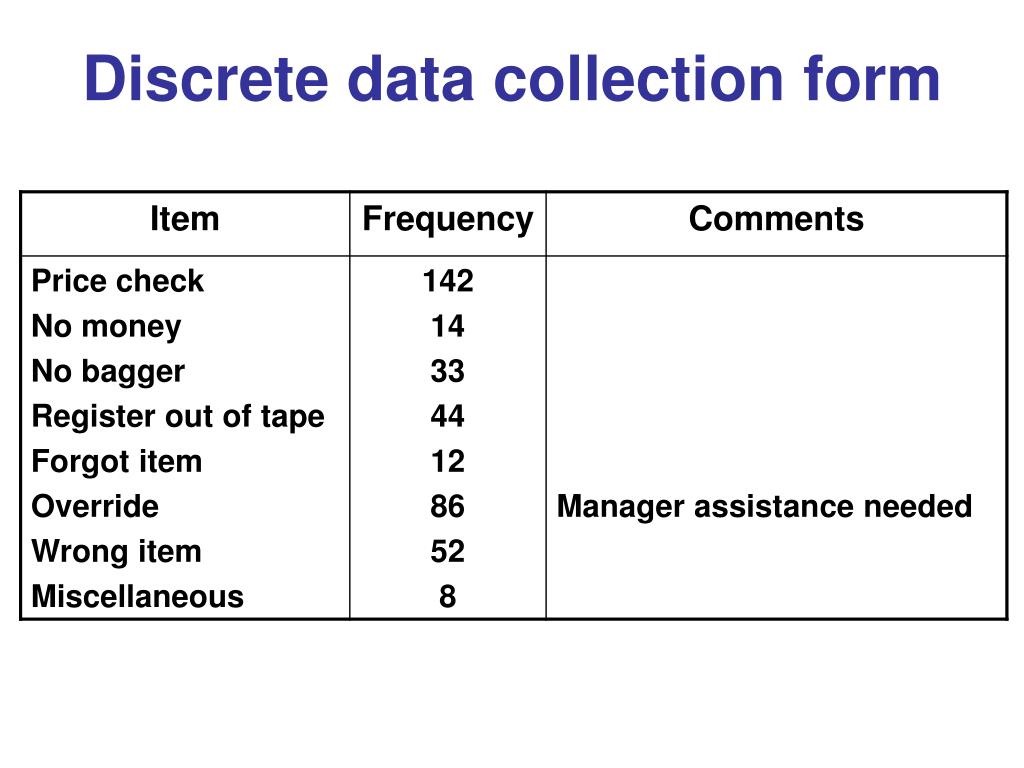
#POINT MEASURE DISCRETE HOW TO#
5.2 How to define random variable and probability distribution - an example.5.1.2 Probability distribution (function).5.1 Random variable and probability distribution - definitions.5 Random variables and probability distributions.4.2.5 Conditional Probability and Independence.4.2.2 Essential definitions and concepts.4.1.12 Permutations and Combinations with Bounded Repetition.4 Introduction to statistical inference.3.22.3 Plot the data from the above example using histograms and smooth density curves.3.22.2 Box plot - example (compare the box plots).3.20 Histogram for the binomial distribution (1).3.19.1 Construction of the density histogram (1).

3.19 Density histogram and frequency histogram. 3.18 Three types of histograms are used:. 3.17 Frequency distribution table and histogram. 3.15 Basic methods of data visualization. 3.11 Finding mean and standard deviation. 3.10 Parameter and statistic - summary of symbols. 3.9 Useful formulas (descriptive statistics). 3.7.3 Basic measures of spread/dispersion. 3.7.2 Which measures of central tendency are appropriate for numerical and categorical data. 3.7.1 Basic measures of central tendency. 3.6 Frequency distribution with intervals (for grouped data). 3.4 Tabular presentation of data distributions. 3.2.1 Types of data and levels of measurement - intuitions. 3.1.2 Levels of measurement (scales of measurement). 3.1 Types of data and the scales of measurement. 2.13.3 Machine learning approaches - visual guide. 2.13.2 Make predictions or decisions using ML. 2.13 Relevant modern application of statistical theory: Machine learning - the conceptual introduction. 2.11.2 Various types of bias in statistical analysis. 2.11.1 Sampling errors and systematic bias. 2.10 Descriptive and inferential statistics. 2.9 Statistical research design - an example of a simple experiment. 2.8 Experimental and observational studies. 2.7 Statistical study - essential steps. 2.2.1 Conceptualisation and operationalisation. 2.2 Constructs and operational definitions. 1.2.7 Integral as an area - intuitive explanation. 1.2.1 Algebra review - some basic rules. 1.2 Review of some mathematical concepts used in statistics and data science. 1.1 Motivation - two reasons why you should learn statistics and data analysis methods?.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
